What is AWS Event Bridge?
AWS Event Bridge is a serverless event bus service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows you to route events between AWS services, your applications, and third-party SaaS applications. It provides a central location for your applications to publish and receive events, making it easier to build event-driven architectures.
It can react to state changes in resources including AWS and non-AWS resources.
How does AWS Event Bridge work?
AWS Event Bridge works by routing events between different AWS services, applications, and third-party SaaS applications. The event bus is the central component of Event Bridge, which provides a way to route events from different sources to different targets.
An event source is a service or application that generates events, and an event target is a service or application that receives events. You can set up rules in Event Bridge to route events from an event source to one or more event targets.
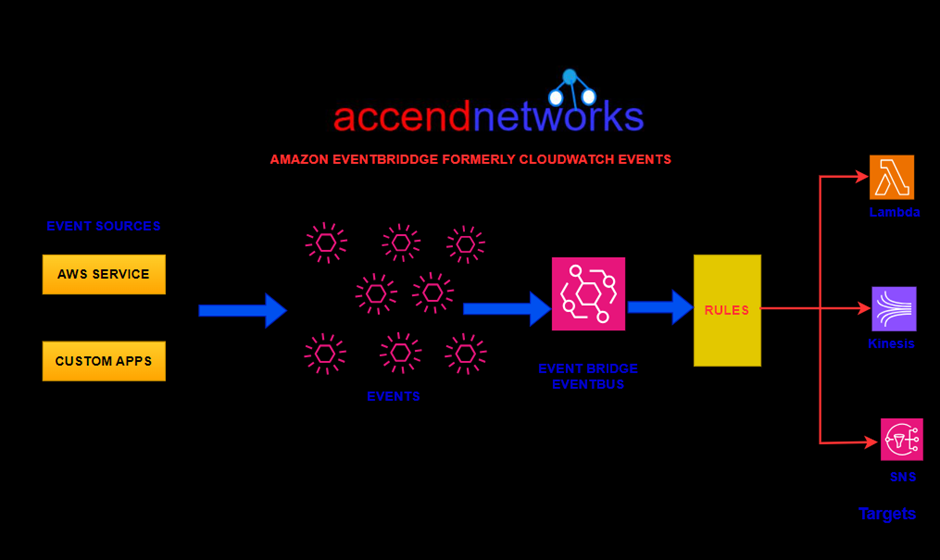
From the above architectural diagram, with AWS event bridge we have event sources, and state change to those resources gets sent as events to what we call an event bridge event bus. Information is then processed by rules and those rules can then send information through to various destinations.
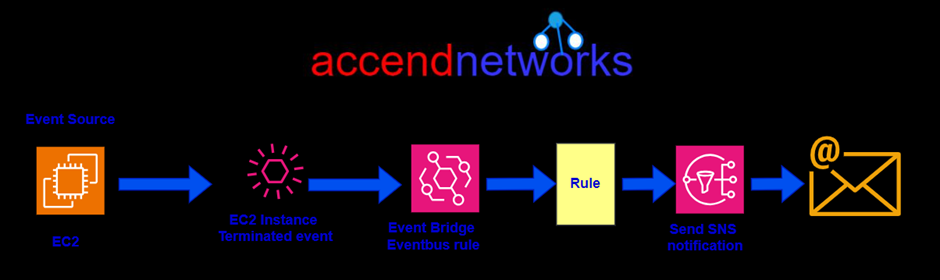
Let’s a gain look at another example, let’s say we have an EC2 instance as an event source and an event happens. That event is a termination event of an ec2 instance that gets forwarded to the event bridge Event Bus. A rule gets processed, and that rule then gets sent through to a destination, in this case, an SNS topic after which an SNS notification gets sent through to an email address
Terms associated with Event Bridge
Events: An event indicates a change in an environment. For. e.g. Change of an EC2 instance from pending to running.
Rules: Incoming events route to targets only if they match the rule that is specified.
Targets: A target can be Lambda functions, Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, SNS, SQS, Pipelines in CICD, Step Functions, etc that receive events in JSON format.
Event Buses: The Event Bus receives an event. When you create a rule, you associate it with a specific event bus, and the rule is matched only to events received by that event bus.
When an event is generated by an event source, it is sent to the Event Bridge event bus. If the event matches one or more rules that you’ve defined, EventBridge forwards the event to the corresponding event targets.
Now let’s make our hands dirty.
Log into the AWS management console, launch an instance, and copy the instance ID.